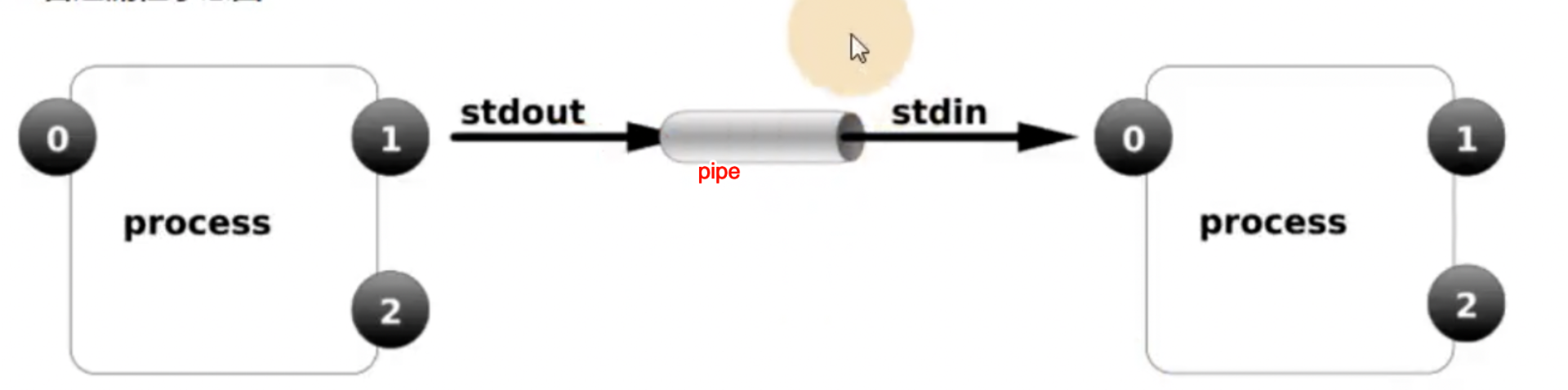
Linux管道
hexo(5)next主题开启图片放大功能
Notepad--(Ndd)跨平台文本编辑器
Notepad–(简称 Ndd,也包含 Subtwo 版本)是一款由中国开发者“爬山虎”(GitHub 用户名 cxasm)使用 C++ 语言开发的跨平台文本编辑器,目标是打造一款“中国人自己的编辑器”,并在功能和体验上超越经典的 Notepad++。它支持 Windows、Linux 和 macOS 三大主流操作系统,特别注重对国产操作系统(如统信 UOS、麒麟 Linux)以及 macOS 的适配和优化。
notepadd–
original-ks.cfg作用
CentOS 7下anaconda-ks.cfg配置
用于自动化安装 CentOS 7 的 Kickstart 文件 (anaconda-ks.cfg),通常用于配置虚拟机(如 Vagrant 环境)或物理机的操作系统安装过程。它定义了安装选项、分区设置、软件包选择以及安装后的配置脚本。
anaconda-ks.cfg
#version=DEVEL
# System authorization information
auth --enableshadow --enablemd5
# Install OS instead of upgrade
install
# Use text mode install
text
# Firewall configuration
firewall --disabled
firstboot --disable
ignoredisk --only-use=vda
# Keyboard layouts
# old format: keyboard us
# new format:
keyboard --vckeymap=us --xlayouts=''
# System language
lang en_US.UTF-8
# Network information
network --bootproto=dhcp --device=eth0 --activate
network --hostname=localhost.localdomain
# Reboot after installation
reboot
repo --name="koji-override-0" --baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/7/extras/x86_64/
repo --name="koji-override-1" --baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/7/updates/x86_64/
# Use network installation
url --url="http://mirror.centos.org/centos/7/os/x86_64/"
# Root password
rootpw --plaintext vagrant
# SELinux configuration
selinux --enforcing
# System services
services --enabled="vmtoolsd,chronyd"
# Do not configure the X Window System
skipx
# System timezone
timezone UTC --isUtc
user --name=vagrant --password=vagrant
# System bootloader configuration
bootloader --append="no_timer_check console=tty0 console=ttyS0,115200n8 net.ifnames=0 biosdevname=0 elevator=noop crashkernel=auto" --location=mbr --timeout=1 --boot-drive=vda
# Clear the Master Boot Record
zerombr
# Partition clearing information
clearpart --all --drives=vda
# Disk partitioning information
part / --asprimary --fstype="xfs" --ondisk=vda --size=40959
%post
# configure swap to a file (fallocate doesn't work with c7 xfs)
dd if=/dev/zero of=/swapfile bs=1M count=2048
chmod 600 /swapfile
mkswap /swapfile
echo "/swapfile none swap defaults 0 0" >> /etc/fstab
# sudo
echo "%vagrant ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL" > /etc/sudoers.d/vagrant
chmod 0440 /etc/sudoers.d/vagrant
# Fix for https://github.com/CentOS/sig-cloud-instance-build/issues/38
cat > /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 << EOF
DEVICE="eth0"
BOOTPROTO="dhcp"
ONBOOT="yes"
TYPE="Ethernet"
PERSISTENT_DHCLIENT="yes"
EOF
# sshd: disable password authentication and DNS checks
ex -s /etc/ssh/sshd_config <<EOF
:%substitute/^\(PasswordAuthentication\) yes$/\1 no/
:%substitute/^#\(UseDNS\) yes$/&\r\1 no/
:update
:quit
EOF
cat >>/etc/sysconfig/sshd <<EOF
# Decrease connection time by preventing reverse DNS lookups
# (see https://lists.centos.org/pipermail/centos-devel/2016-July/014981.html
# and man sshd for more information)
OPTIONS="-u0"
EOF
# Default insecure vagrant key
mkdir -m 0700 -p /home/vagrant/.ssh
echo "ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAQEA6NF8iallvQVp22WDkTkyrtvp9eWW6A8YVr+kz4TjGYe7gHzIw+niNltGEFHzD8+v1I2YJ6oXevct1YeS0o9HZyN1Q9qgCgzUFtdOKLv6IedplqoPkcmF0aYet2PkEDo3MlTBckFXPITAMzF8dJSIFo9D8HfdOV0IAdx4O7PtixWKn5y2hMNG0zQPyUecp4pzC6kivAIhyfHilFR61RGL+GPXQ2MWZWFYbAGjyiYJnAmCP3NOTd0jMZEnDkbUvxhMmBYSdETk1rRgm+R4LOzFUGaHqHDLKLX+FIPKcF96hrucXzcWyLbIbEgE98OHlnVYCzRdK8jlqm8tehUc9c9WhQ== vagrant insecure public key" >> /home/vagrant/.ssh/authorized_keys
chmod 600 /home/vagrant/.ssh/authorized_keys
chown -R vagrant:vagrant /home/vagrant/.ssh
# Fix for issue #76, regular users can gain admin privileges via su
ex -s /etc/pam.d/su <<'EOF'
# allow vagrant to use su, but prevent others from becoming root or vagrant
/^account\s\+sufficient\s\+pam_succeed_if.so uid = 0 use_uid quiet$/
:append
account [success=1 default=ignore] \\
pam_succeed_if.so user = vagrant use_uid quiet
account required pam_succeed_if.so user notin root:vagrant
.
:update
:quit
EOF
# systemd should generate a new machine id during the first boot, to
# avoid having multiple Vagrant instances with the same id in the local
# network. /etc/machine-id should be empty, but it must exist to prevent
# boot errors (e.g. systemd-journald failing to start).
:>/etc/machine-id
echo 'vag' > /etc/yum/vars/infra
# Blacklist the floppy module to avoid probing timeouts
echo blacklist floppy > /etc/modprobe.d/nofloppy.conf
chcon -u system_u -r object_r -t modules_conf_t /etc/modprobe.d/nofloppy.conf
# Customize the initramfs
pushd /etc/dracut.conf.d
# Enable VMware PVSCSI support for VMware Fusion guests.
echo 'add_drivers+=" vmw_pvscsi "' > vmware-fusion-drivers.conf
echo 'add_drivers+=" hv_netvsc hv_storvsc hv_utils hv_vmbus hid-hyperv "' > hyperv-drivers.conf
# There's no floppy controller, but probing for it generates timeouts
echo 'omit_drivers+=" floppy "' > nofloppy.conf
popd
# Fix the SELinux context of the new files
restorecon -f - <<EOF
/etc/sudoers.d/vagrant
/etc/dracut.conf.d/vmware-fusion-drivers.conf
/etc/dracut.conf.d/hyperv-drivers.conf
/etc/dracut.conf.d/nofloppy.conf
EOF
# Rerun dracut for the installed kernel (not the running kernel):
KERNEL_VERSION=$(rpm -q kernel --qf '%{version}-%{release}.%{arch}\n')
dracut -f /boot/initramfs-${KERNEL_VERSION}.img ${KERNEL_VERSION}
# Seal for deployment
rm -rf /etc/ssh/ssh_host_*
hostnamectl set-hostname localhost.localdomain
rm -rf /etc/udev/rules.d/70-*
%end
%packages --instLangs=en
bash-completion
bzip2
chrony
cifs-utils
deltarpm
hyperv-daemons
kexec-tools
man-pages
nfs-utils
open-vm-tools
rsync
yum-utils
-aic94xx-firmware
-alsa-firmware
-alsa-tools-firmware
-dracut-config-rescue
-ivtv-firmware
-iwl100-firmware
-iwl1000-firmware
-iwl105-firmware
-iwl135-firmware
-iwl2000-firmware
-iwl2030-firmware
-iwl3160-firmware
-iwl3945-firmware
-iwl4965-firmware
-iwl5000-firmware
-iwl5150-firmware
-iwl6000-firmware
-iwl6000g2a-firmware
-iwl6000g2b-firmware
-iwl6050-firmware
-iwl7260-firmware
-iwl7265-firmware
-kexec-tools
-linux-firmware
-microcode_ctl
-plymouth
%end
%addon com_redhat_kdump --enable --reserve-mb='auto'
%end
docker ADD指令
docker镜像构建过程rootfs、scratch含义
1. rootfs(根文件系统)
rootfs 是指 Docker 容器运行时所依赖的根文件系统(root filesystem)。它是容器内部文件系统的起点,包含了容器运行所需的基本目录结构和文件,比如 /bin、/lib、/etc 等。简而言之,rootfs 是容器操作系统的核心部分。
- 来源:在 Docker 中,
rootfs通常来源于镜像(image)。镜像是一个只读的模板,包含了应用程序及其依赖的操作系统文件。容器启动时,Docker 会基于镜像的rootfs创建一个可写的容器层。 - 分层结构:Docker 使用 UnionFS(联合文件系统)将多个只读层(如镜像层)和一个可写层(容器层)组合成完整的
rootfs。 - 作用:提供容器运行时的文件系统环境,确保容器内的进程能够访问所需的文件和库。
rootfs relase
openwrt磁盘空间扩容汇总
- 刷openwrt启动前
- 刷openwrt启动后
release
- generic-ext4-combined-legacy
- generic-ext4-combined-efi
- generic-squashfs-legacy
- generic-squashfs-efi
openwrt-download
fdisk用法
在 Linux 中,fdisk 是一个用于管理磁盘分区的命令行工具。它主要用于创建、删除、修改硬盘分区表,适用于 MBR(Master Boot Record)分区表格式的磁盘。虽然对于较新的 GPT(GUID Partition Table)分区表,fdisk 也提供了支持,但某些情况下可能需要使用更专用的工具如 gdisk。
介绍
fdisk 是 Linux 系统中的一个交互式分区工具,广泛用于磁盘管理。它允许用户查看当前分区布局,并对分区进行操作,例如添加新分区、删除旧分区、更改分区类型等。运行 fdisk 时,通常需要指定目标磁盘(如 /dev/sda),并且需要超级用户权限(sudo)。
RDMA是什么
RDMA(远程直接内存访问,Remote Direct Memory Access)是一种网络通信技术,允许一台计算机直接访问另一台计算机的主内存,而无需经过目标计算机的处理器、缓存或操作系统。这种方法通过绕过传统的网络协议栈(如TCP/IP),显著降低了延迟、提高了带宽,并减少了CPU的负载。
RDMA的核心特点
- 零拷贝(Zero-copy):数据直接从一台计算机的内存传输到另一台,无需中间缓冲区。
- 内核绕过(Kernel bypass):数据传输无需操作系统内核参与,减少了上下文切换的开销。
- 低延迟和高吞吐量:非常适合需要快速响应的应用场景,如高性能计算(HPC)、云计算和分布式存储系统。