Fedora(5)Fedora Media Writer写iso软件
Posted on
Fedora(4)workstation体验
Posted on
Fedora Workstation Live 42 Beta 于 2025 年 3 月 18 日发布,目前仍处于测试阶段,因此安装过程中可能会遇到一些小问题,但整体体验已经非常接近最终版本。
env
- virtualbox-v7.1.6
- Fedora-Workstation-Live-x86_64-42_Beta-1.4.iso
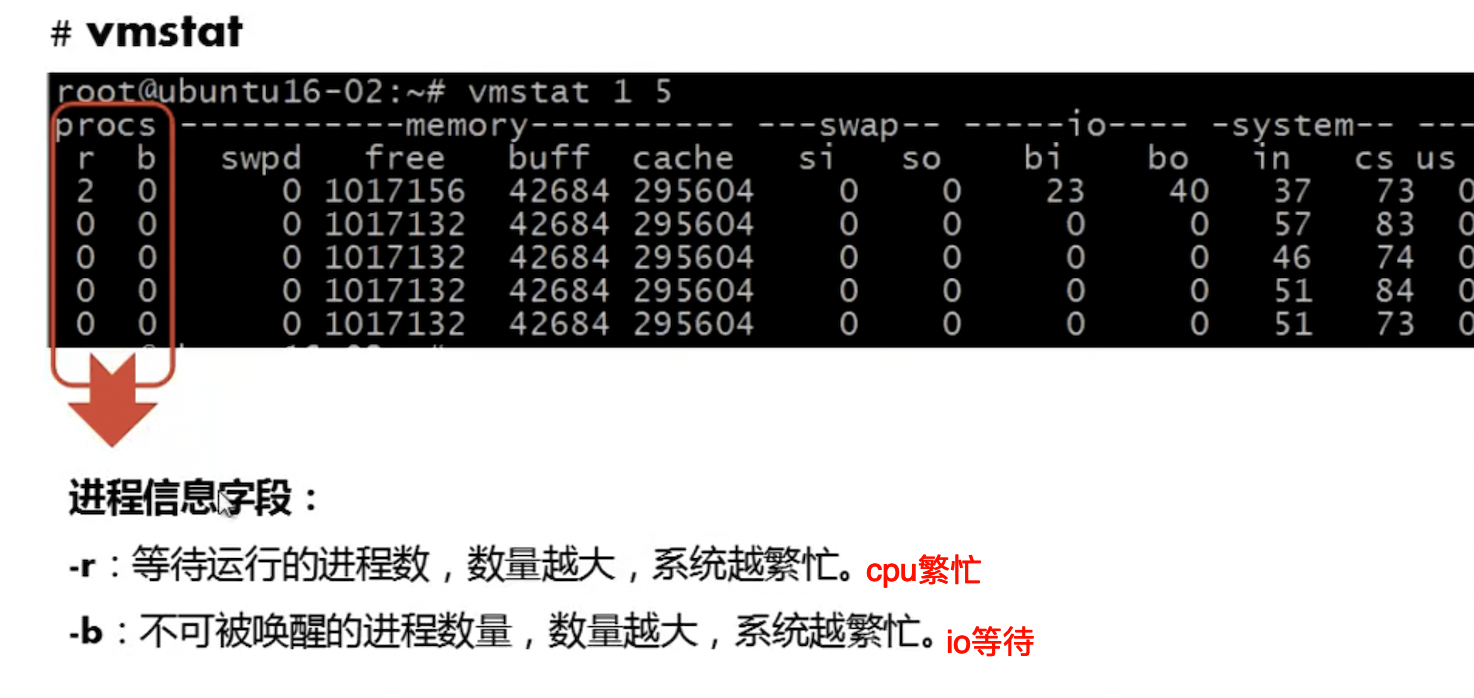
vmstat输出字段解读
Posted on
ubuntu(10)dpkg命令
Posted on
在 Ubuntu 或其他基于 Debian 的系统中,**dpkg 是一个底层的包管理工具,用于处理 .deb 包**的安装、卸载、查询等操作。
dpkg help
root@vgt-ubuntu-10:~# dpkg --help
Usage: dpkg [<option>...] <command>
Commands:
-i|--install <.deb file name>... | -R|--recursive <directory>... ### 安装
--unpack <.deb file name>... | -R|--recursive <directory>...
-A|--record-avail <.deb file name>... | -R|--recursive <directory>...
--configure <package>... | -a|--pending
--triggers-only <package>... | -a|--pending
-r|--remove <package>... | -a|--pending ### 移除
-P|--purge <package>... | -a|--pending ### 移除包及配置
-V|--verify [<package>...] Verify the integrity of package(s).
--get-selections [<pattern>...] Get list of selections to stdout.
--set-selections Set package selections from stdin.
--clear-selections Deselect every non-essential package.
--update-avail [<Packages-file>] Replace available packages info.
--merge-avail [<Packages-file>] Merge with info from file.
--clear-avail Erase existing available info.
--forget-old-unavail Forget uninstalled unavailable pkgs.
-s|--status [<package>...] Display package status details.
-p|--print-avail [<package>...] Display available version details.
-L|--listfiles <package>... List files 'owned' by package(s). ### 列出包内文件
-l|--list [<pattern>...] List packages concisely.
-S|--search <pattern>... Find package(s) owning file(s).
-C|--audit [<package>...] Check for broken package(s).
--yet-to-unpack Print packages selected for installation.
--predep-package Print pre-dependencies to unpack.
--add-architecture <arch> Add <arch> to the list of architectures.
--remove-architecture <arch> Remove <arch> from the list of architectures.
--print-architecture Print dpkg architecture.
--print-foreign-architectures Print allowed foreign architectures.
--assert-help Show help on assertions.
--assert-<feature> Assert support for the specified feature.
--validate-<thing> <string> Validate a <thing>'s <string>.
--compare-versions <a> <op> <b> Compare version numbers - see below.
--force-help Show help on forcing.
-Dh|--debug=help Show help on debugging.
-?, --help Show this help message.
--version Show the version.
Validatable things: pkgname, archname, trigname, version.
Use dpkg with -b, --build, -c, --contents, -e, --control, -I, --info,
-f, --field, -x, --extract, -X, --vextract, --ctrl-tarfile, --fsys-tarfile
on archives (type dpkg-deb --help).
Options:
--admindir=<directory> Use <directory> instead of /var/lib/dpkg.
--root=<directory> Install on a different root directory.
--instdir=<directory> Change installation dir without changing admin dir.
--pre-invoke=<command> Set a pre-invoke hook.
--post-invoke=<command> Set a post-invoke hook.
--path-exclude=<pattern> Do not install paths which match a shell pattern.
--path-include=<pattern> Re-include a pattern after a previous exclusion.
-O|--selected-only Skip packages not selected for install/upgrade.
-E|--skip-same-version Skip packages whose same version is installed.
-G|--refuse-downgrade Skip packages with earlier version than installed.
-B|--auto-deconfigure Install even if it would break some other package.
--[no-]triggers Skip or force consequential trigger processing.
--verify-format=<format> Verify output format (supported: 'rpm').
--no-pager Disables the use of any pager.
--no-debsig Do not try to verify package signatures.
--no-act|--dry-run|--simulate
Just say what we would do - don't do it.
-D|--debug=<octal> Enable debugging (see -Dhelp or --debug=help).
--status-fd <n> Send status change updates to file descriptor <n>.
--status-logger=<command> Send status change updates to <command>'s stdin.
--log=<filename> Log status changes and actions to <filename>.
--ignore-depends=<package>[,...]
Ignore dependencies involving <package>.
--force-<thing>[,...] Override problems (see --force-help).
--no-force-<thing>[,...] Stop when problems encountered.
--refuse-<thing>[,...] Ditto.
--abort-after <n> Abort after encountering <n> errors.
--robot Use machine-readable output on some commands.
Comparison operators for --compare-versions are:
lt le eq ne ge gt (treat empty version as earlier than any version);
lt-nl le-nl ge-nl gt-nl (treat empty version as later than any version);
< << <= = >= >> > (only for compatibility with control file syntax).
Use 'apt' or 'aptitude' for user-friendly package management.
procps(2)vmstat命令
Posted on
procps(1)包介绍
Posted on
procps 是一个在 Linux 系统中广泛使用的软件包,主要提供了一系列用于监控和管理系统进程的工具。它是许多 Linux 发行版(包括 Ubuntu)的核心组件之一。procps 的工具主要依赖于 /proc 文件系统(Linux 内核提供的虚拟文件系统),通过读取其中的信息来展示系统状态、进程信息等。
在 Ubuntu 中,procps 包通常默认安装,因为它包含了一些基础且常用的命令行工具,例如 ps、top、kill 等。如果没有安装,可以通过以下命令安装:
1 | sudo apt update |
sysstat(5)pidstat命令
Posted on
Edited on
sysstat(1)系统性能分析介绍
Posted on
在 Ubuntu 中,sysstat 是一个非常有用的软件包,提供了系统性能监控和统计工具。它包含一系列命令行工具,可以帮助用户收集和分析系统的资源使用情况,如 CPU、内存、磁盘 I/O、网络等。
1.主要功能
sysstat 包提供了以下核心工具:
sar(System Activity Reporter)
- 用于收集、报告和保存系统的活动统计信息。
- 可以监控 CPU 使用率、内存使用、磁盘 I/O、网络流量等。
- 数据可以实时显示,也可以存储下来供后续分析。
iostat
- 提供 CPU 和磁盘 I/O 的统计信息。
- 常用于分析磁盘性能和系统负载。
mpstat
- 显示多处理器系统的 CPU 使用情况。
- 对于多核系统尤为有用,可以查看每个核心的性能数据。
pidstat
- 提供每个进程的资源使用统计,如 CPU、内存和 I/O。
- 适合排查特定进程的性能问题。
sadf
- 将
sar收集的数据转换为多种格式(如 CSV、XML),便于进一步分析或可视化。
- 将
openobserve(1)介绍及架构
Posted on
Edited on
pstree进程数命令
Posted on
ubuntu(9)apt-get vs apt
Posted on
Edited on
在 Ubuntu 中,apt-get 和 apt 都是用于管理软件包的工具,但它们有一些区别,主要体现在用途、设计目标和使用体验上。
1. 起源和目的
apt-get:- 是 Debian 系系统(包括 Ubuntu)中**较早期的包管理工具,基于底层的
dpkg**。 - 设计初衷是给脚本和高级用户提供强大的功能,功能全面但命令较繁琐。
- 更适合需要细粒度控制或在脚本中使用的场景。
- 是 Debian 系系统(包括 Ubuntu)中**较早期的包管理工具,基于底层的
apt:- 是较新的工具,首次在 Debian 8 和 Ubuntu 16.04 中引入。
- 它是
apt-get和其他工具(如apt-cache)的一个高级封装,旨在提供更简洁、用户友好的命令行界面。 - 主要面向终端用户,而不是脚本或自动化任务。